Generating Product Improvement Ideas Using LLMs
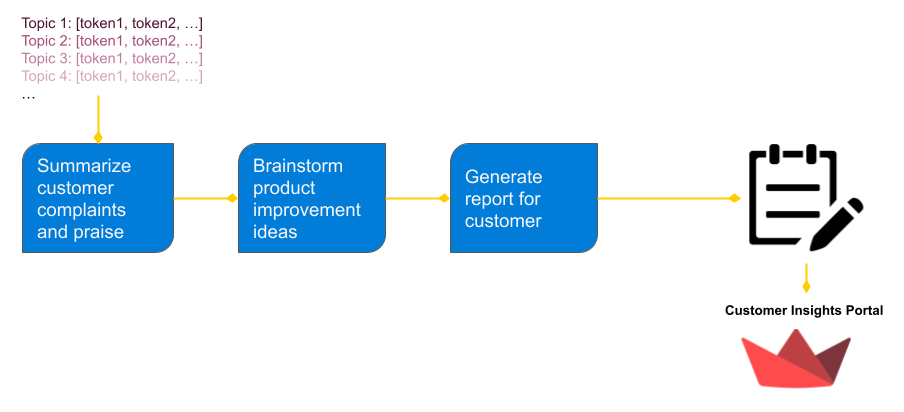
This app is a hypothetical AI system that delivers product insights to Flipkart sellers, including key patterns in customer complaints and praise, as well as recommendations to improve the product.
Approach
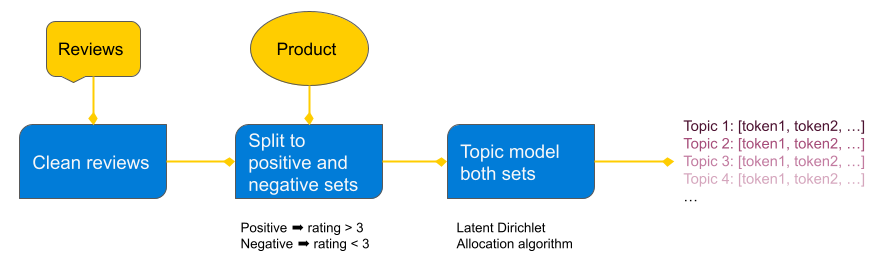
The general approach is to identify the dominant themes in positive and negative customer reviews for each product and feed the customer complaint patterns into GPT to produce product improvement recommendations. The Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) algorithm is an effective technique for extracting out “topics” from a corpus. I assume negative customer reviews can be distilled into a small set of common complaints that a topic modeling algorithm like LDA can find, and this reduced representation of the corpus can be fed to an LLM model to brainstorm product improvement ideas.
Why do topic modeling rather than sending GPT all the reviews?
One might wonder why we can’t just send GPT all the reviews and ask it to ideate product improvements? Technically, we can, but data science must consider the costs of scaling such a solution. OpenAI charges on a per-token basis, so sending all reviews would be orders of magnitude more expensive. We can get similar results by collapsing an entire corpus of product reviews into a fixed number of tokens by applying topic modeling beforehand.
For example, in this application, the number of tokens sent to GPT is just 50 tokens (5 topics and 5 tokens per topic for both positive and negative reviews). In total, there are 8,101,246 tokens in this corpus of product reviews. By applying LDA (10 topics per product, 5 tokens per topic), I reduce this token count to 15,825 tokens! That is a 99.8% reduction in costs. That’s not much for this dataset, but it will be after scaling to all sellers and products on Flipkart, not to mention the added latency of sending GPT all of those tokens.
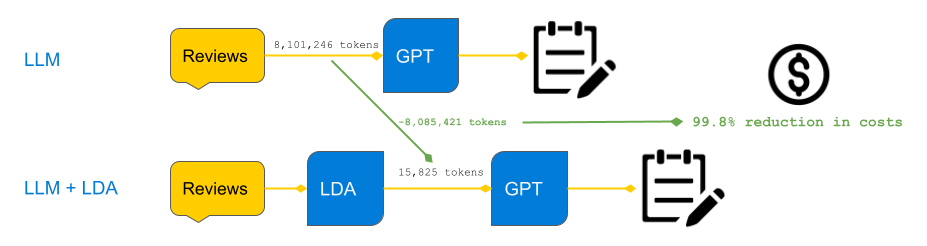
This is an important demonstration of how data scientists should think about scaling solutions involving LLMs. It’s not wise to brute force NLP problems with LLMs when basic preprocessing and token reduction methods prior to the LLM prompts can slash most of the costs and latency in a scaled solution.